Spoofing in Radar ECM
Spoofing consists in the generation of a programmed number of false echoes without specific kinematic law with constant or random spacing.
False echo delays are periodically refreshed to avoid the presence of annular (constant range lines) in radar PPI.
Spoofing generation is obtained through repetition of jamming pulses that are obtained from a stored slice of threat signal:
the detection and storage of countered Radar waveform is necessary to jam.
When counteracting a scanning radar, the jamming waveforms are transmitted after lobe acquisition and continues until the radar lobe is lost.
Non-coherent Spoofing, actually synthesized pulse train, can be limited by the lack of synchronization with radar PRI and radiated frequency.
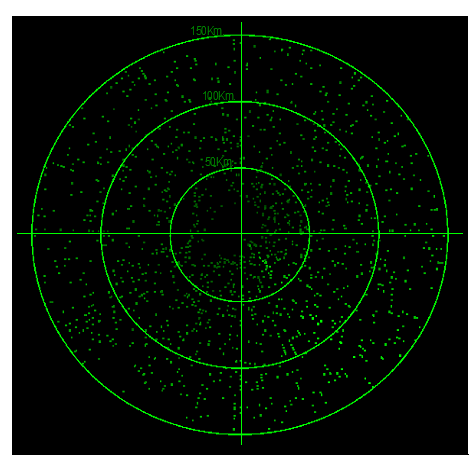
Figure 1: Spoofing effect in a Radar PPI
Spoofing technique needs to generate random delay patterns. If the delay pattern for a maximum number of false echoes is less than the number of Spoofing false echoes, then the basic pattern can be repeated until the programmed number of false echoes is reached.
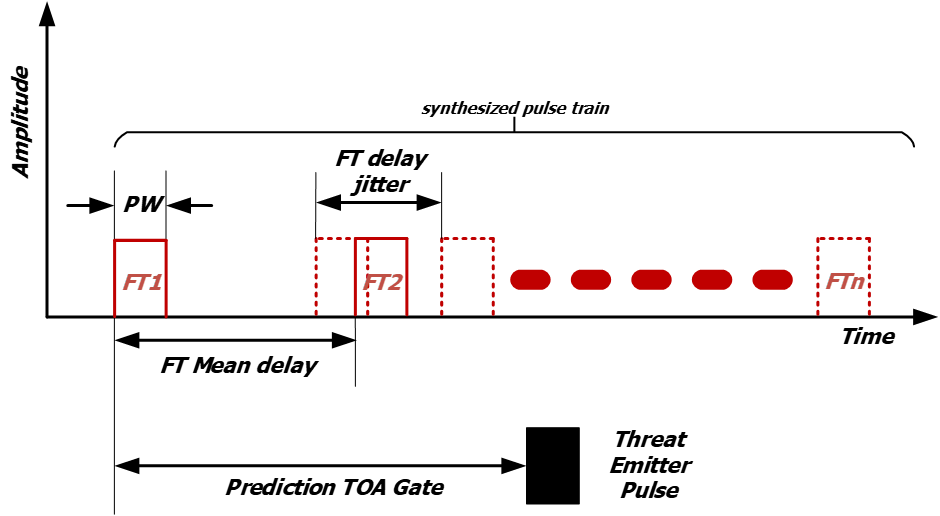
Figure 2: Spoofing, synthesized pulse train
Spoofing is normally programmed with a high duty cycle to produce a high number of false echoes that, in addition to increasing false detections, can affect the Radar adapted threshold (Radar adapted threshold is optimized for continuous background noise or clutter and real echoes can be masked.
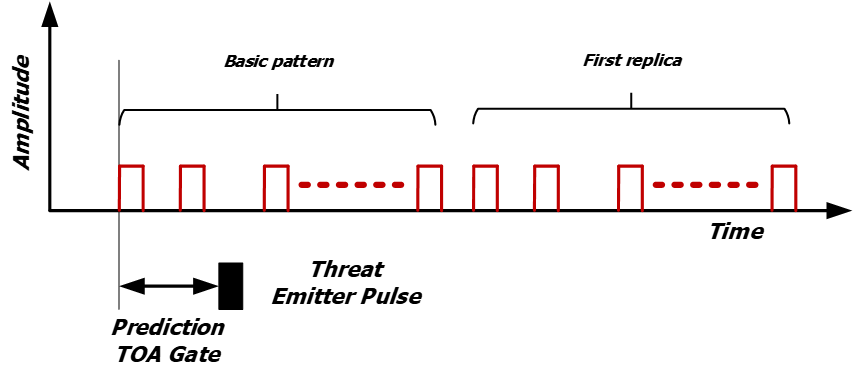
Figure 3: Spoofing, programmed replicas