Operational Support Centre for SIGINT Missions
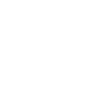
Modern EW operations have evolved to control information flow based on the Electro Magnetic Spectrum to ensure friendly freedom of action and to diminish or deny the enemy’s ability to operate, progressing from EW Ops to EMSO (Electro Magnetic Spectrum Operation) and becoming a pillar of C4ISTAR and System of Systems.
Furthermore, the expected increase in the use of UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles) by symmetric and asymmetric forces and their deployment across all types of theatres has created the need to upgrade Area Protection with an EW-based detection, identification and soft kill capability to complement Ground Based Air Defence (GBAD) → Soft Kill for Ground Based Air Defence (SKGBAD).
Within EMSO we can also define a further level of integration made by the close convergence of EW Ops and Cyber Ops (aka CEMA) that has created a new order of battle oriented to disrupt or degrade enemy capabilities in military operations that are increasingly net-centric and computer-centric.
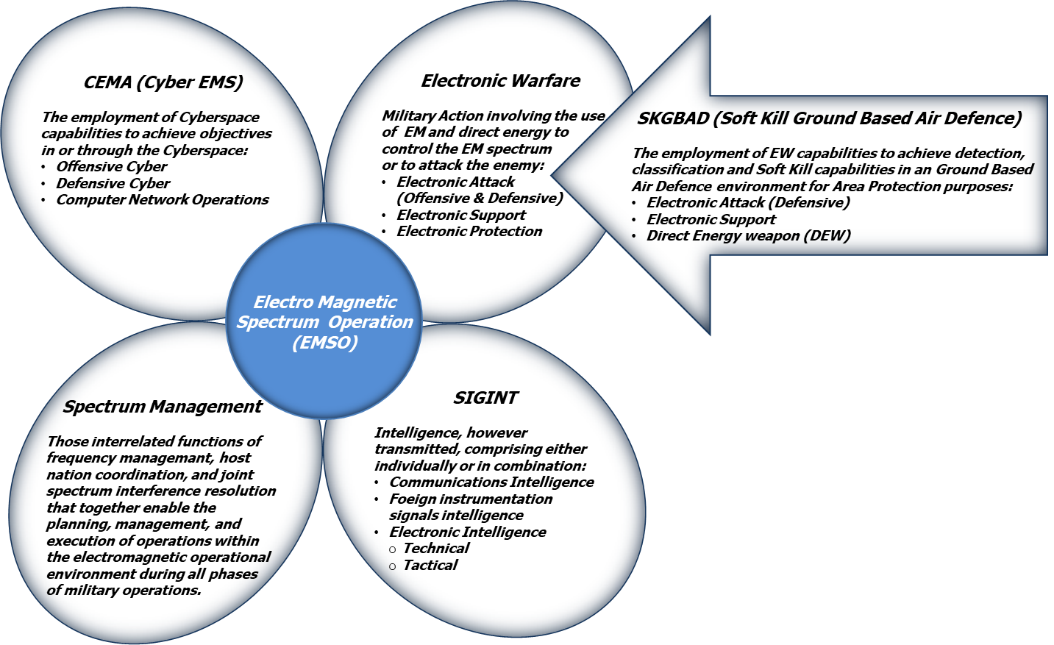
Figure 1: EMSO with Ground Air Defence specialization for EW
The dignity of EW has increased to become a System of Systems, transforming itself into EMSO, the mix of classic old EW, Net-Centric Ops, SIGINT, Cyber Ops, Spectrum Ops and SKGBAD requiring the ability to operate in a distributed, cognitive and collaborative context.
The more complex, integrated and interconnected operative environment requires a parallel evolution of an innovative concept of Operational Support that becomes Information Operational Support and includes in a collaborative, cognitive and net-centric way all the different platforms, all the different technologies and all the different scenarios in a single integrated architecture.
To this must be added a powerful real-time system management to be realised by replicating part of the Central Operational Support capabilities to distributed systems in the operational scenario, resident in the platforms, allowing fast analysis capabilities to follow the rapid evolution of the tactical situation.
The Operational Support thus becomes a distributed capability in a net-centric configuration and itself rises to the status of a System of Systems.
This transformation cannot begin else than starting from the SIGINT Operational Support.
The SIGINT Operational Support Centre (SOSC) is part of the Mission Ground Support Segment (MGSS), a cloud of Mission Support capabilities including also the specific EW Operational Support (EWOC, EW Operational Centre) for the Armed Forces and for Cyber EW (CEMA), and must be flexible and tailored to customer’s needs in terms of modularity and capability to interface National Intelligence Centres.
SIGINT is part of EMSO and refers to all the processing activities such as collection, evaluation, analysis, dissemination and includes ELINT (Electromagnetic radar signal intelligence) and COMINT (Electromagnetic Communication signal intelligence).
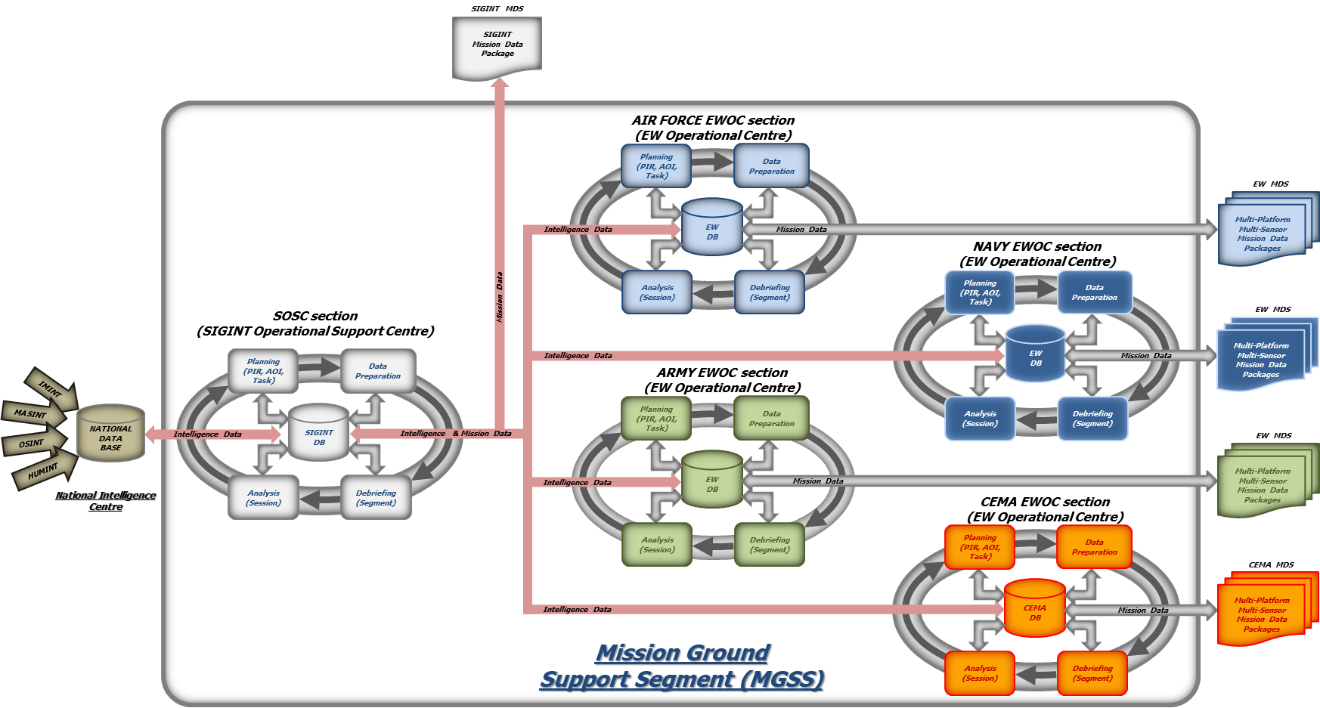
Figure 2: Schematic view of MGSS and interaction with National Data Base and MDS for SIGINT and EW/CEMA
Signal intelligence is based on sources of information from electromagnetic interceptions coming from different sensors (space (satellite), air platforms (manned or unmanned aircrafts) naval platforms and ground based platforms).
Data acquired and stored during a SIGINT mission are off-line analysed in the Operational Support Centre for Intelligence Data Bases update purposes.
The SIGINT Data Base creates strategic information that are part of the Intelligence information that feed the National Data Base; a selected part of the SIGINT Data Base is used at tactical level to feed the EWOC (EW Operational Centre) to create the a-priori data for the Electronic Order of Battlefield (EOB).
A-priori information’s are made available to the SIGINT Mission for comparison with new detected emissions in real time (RT,) or near-real time (NRT), in both cases a reduced section of the SIGINT Operational Support Centre is embedded in the SIGINT system to allow for rapid analysis for tactical purposes.
The workflow inside the MGSS is organized into two loops:
- The Observe, Orient, Decide and Act (OODA) loop that has the task of defining, planning, tasking, conduct and synchronize the missions by preparing MDS for SIGINT platforms (Intelligence) and for RESM/CESM, RWR, RECM/CECM (Operation).
- The Intelligence Cycle that has the task of data gathering, processing, evaluation and dissemination and is also powered by dedicated software packages tools for COMINT and ELINT (to download data coming from SIGINT platforms and to perform technical and tactical analysis), for the intelligence data coming from the National Data base and for Big Data Analysis.
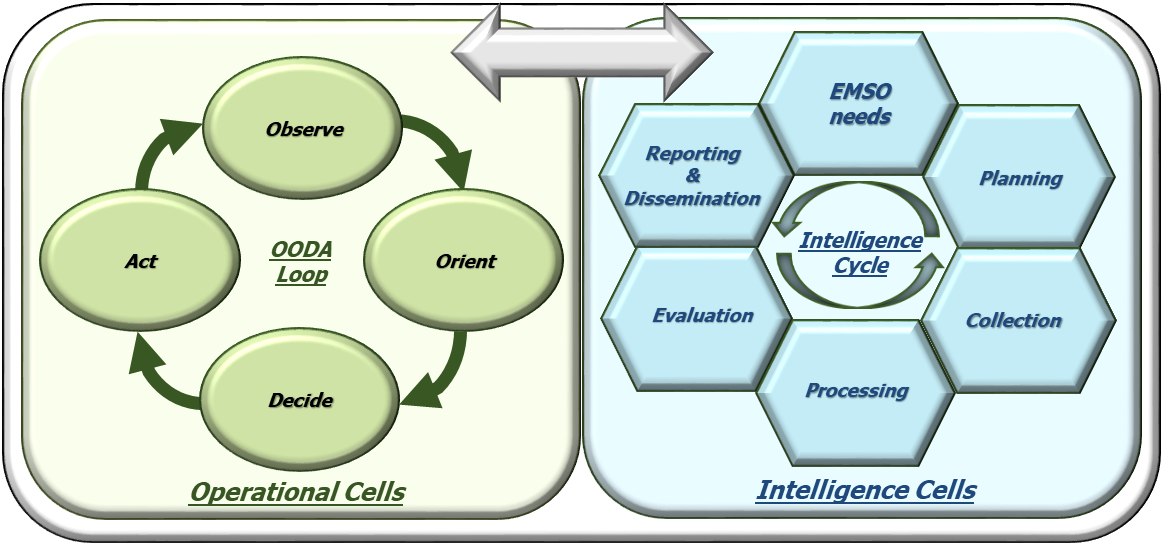
Figure 3: OODA Loop and Intelligence Cycle
The SIGINT Operational Support Centre is an integrated set of HW/SW systems that fully supports the SIGINT missions of the Air-Ground-Naval Systems, for different frequency bands and types (Radar, Communications, EO, IR, etc.).
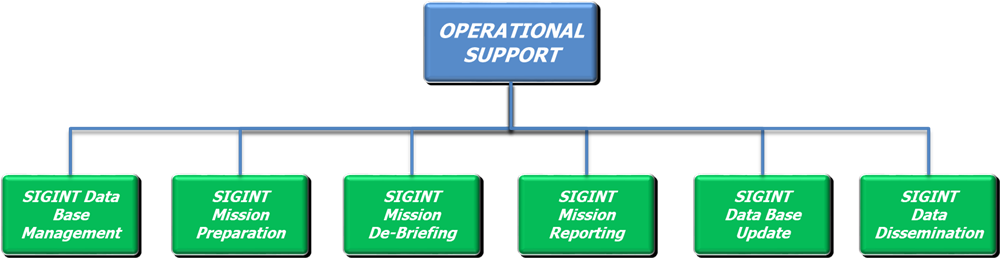
Figure 4: SIGINT Operational Support Structure
It includes all the facilities and functions that are needed for a self-contained approach to modern SIGINT systems management and mission preparation.
SIGINT Operational Support is organized in the following parts:
-
SIGINT Database Management: performs the management and maintenance of the SIGINT DB, which is the repository for technical, tactical and all mission data.
-
SIGINT Pre-Mission Activity (Mission Preparation) composed by:
- Mission Planning: it allows the operator to plan a mission in order to accomplish the assigned operational task, and to satisfy the Mission Commander priority intelligence requirement
-
Mission data Package Generation: generates the SIGINT Library for the mission.
-
SIGINT Post-Mission Activity composed by:
-
Mission Debriefing and Replay: analyses and elaborates the data recorded during the missions.
-
Mission Data Analysis: processes the technical and tactical parameters detected by a SIGINT equipment, compares and associates them with the known parameters of a particular radar system, extracting the essential facts from the mass of raw ELINT/COMINT collected data. It is responsible to generate requests of update to the SIGINT DB.
-
Mission Reporting: the analysis results may be propagated internally to SOSC by the SIGINT DB updating or externally through formatted reports in MS Office Standard representation as Power Point, Word and Excel Data
-
Data Base Update: the mission debriefing and analysis result are used to update the central database in terms of technical and tactical entities
- Data Dissemination: the analysis results can be propagated internally to the SIGINT Operational Support Centre or externally through formatted reports.
-
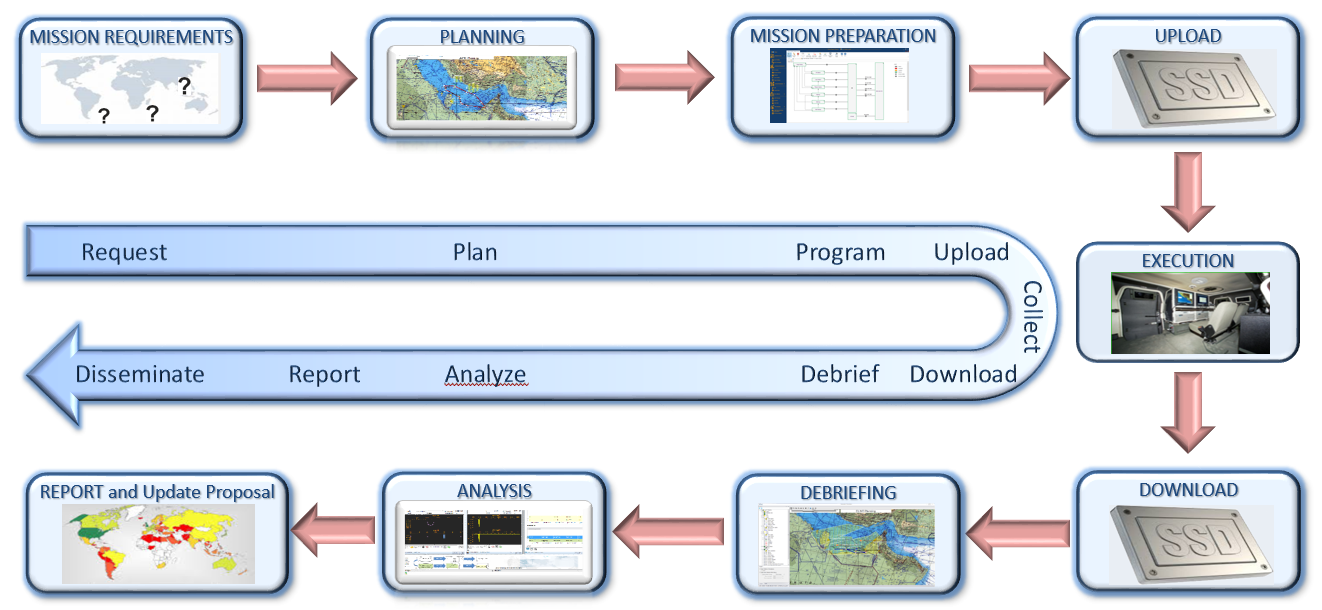
Figure 5: SIGINT Mission Integrated Workflow
The steps performed by the SIGINT Operational Support Centre in case of an ELINT Mission are illustrated in the following:
-
ELINT DB Management
-
Collection Management, Configuration Control, Query and Report
-
Updating and Analysis Result propagation
-
Import/Export on External Interface
-
Support and update CONOPS and requirements
-
The contents of the ELINT DB are designed as collection of CI (Configuration Item) with hierarchical relationship.
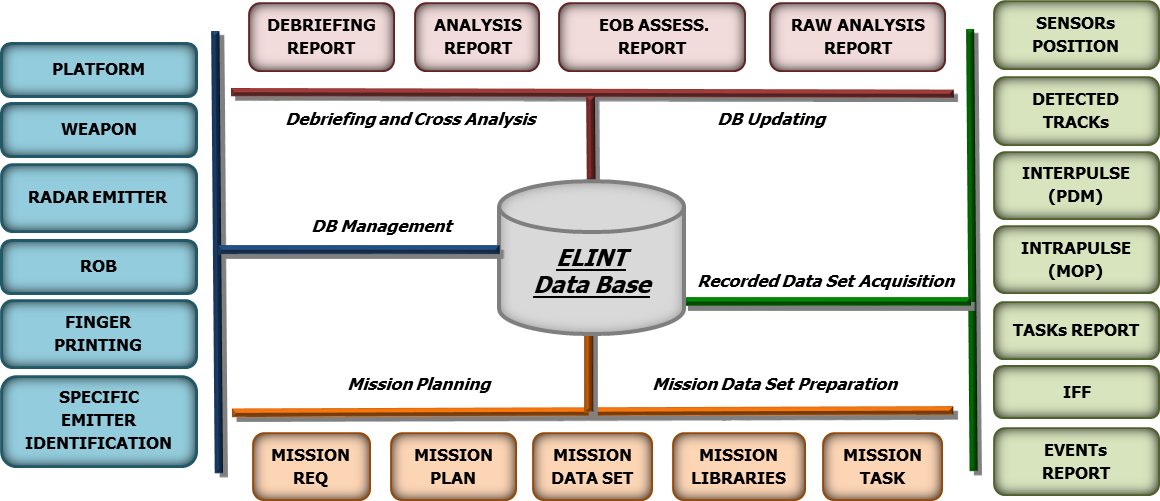
Figure 6: Data contents related to operational phases
The ELINT DB data model is based on the following main sections:
-
-
Technical: Platform, Weapon, RF Emitter, Finger Printing, Specific Emitter Identification (SEI) and Countermeasure
-
Tactical (ROB): Unit, Installation, RADAR Site and Interception
-
Pre Mission Data: MDS (libraries and planning)
-
Post Mission Data: Contact Data, Analysis Data and Status Report
-
The Data Consistency of the structures and their relationships are automatically controlled by SOSC.
The ELINT DB allows to insert Auxiliary information, by means link to standard Files or Image.
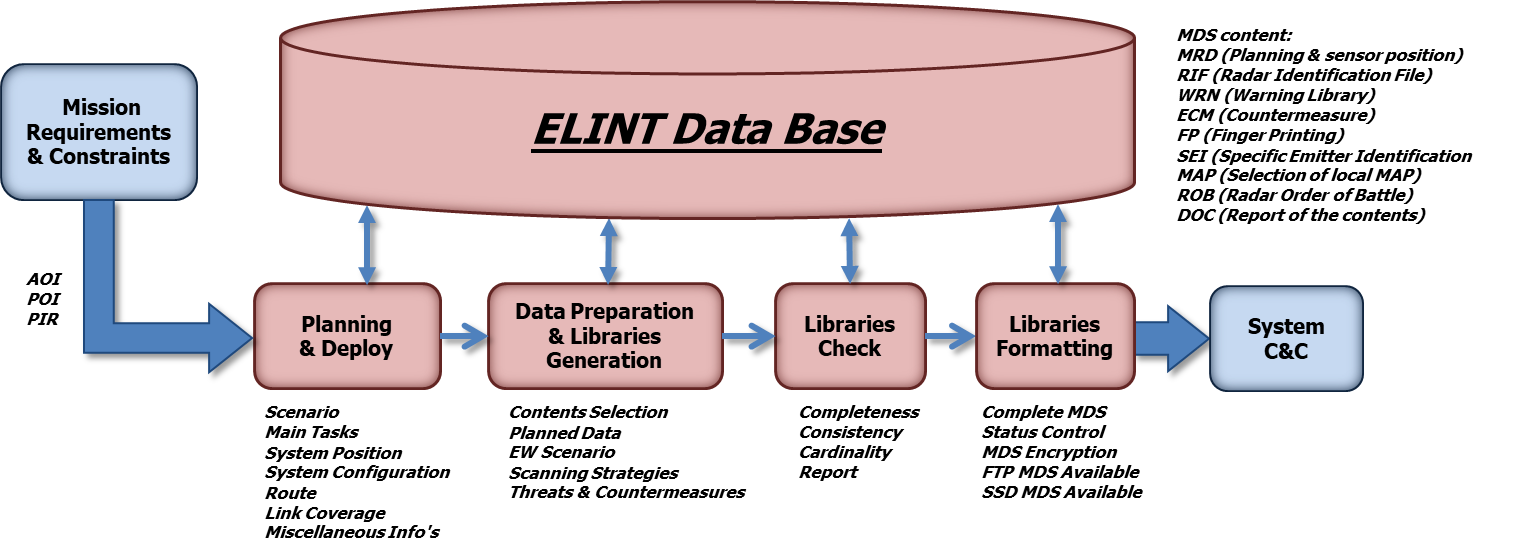
Figure 7: ELINT Pre-Mission Activities
-
ELINT Pre-Mission (Mission Preparation) Activities
The ELINT Mission Preparation context allows the operator to:
-
Mission Planning: the plan of the Mission is based on the requirements and Environmental constraints.
-
Deploy: deploy of assets inside an area with support for visibility and connection (Radio Link and FON).
-
Route, Requirements and Task: the planning data for Air, Ground and Maritime Platforms.
-
Data Preparation: according to the planned mission, the contents of ELINT DB are selected once, then used for all System Libraries.
-
Data Consistency: the different Libraries are checked for completeness and consistency, in order to optimize the Mission result.
-
MDS Formatting: the Libraries and any other Mission Data structure are formatted, encrypted and made available to the target equipment by means SSD support or SFTP Server
-
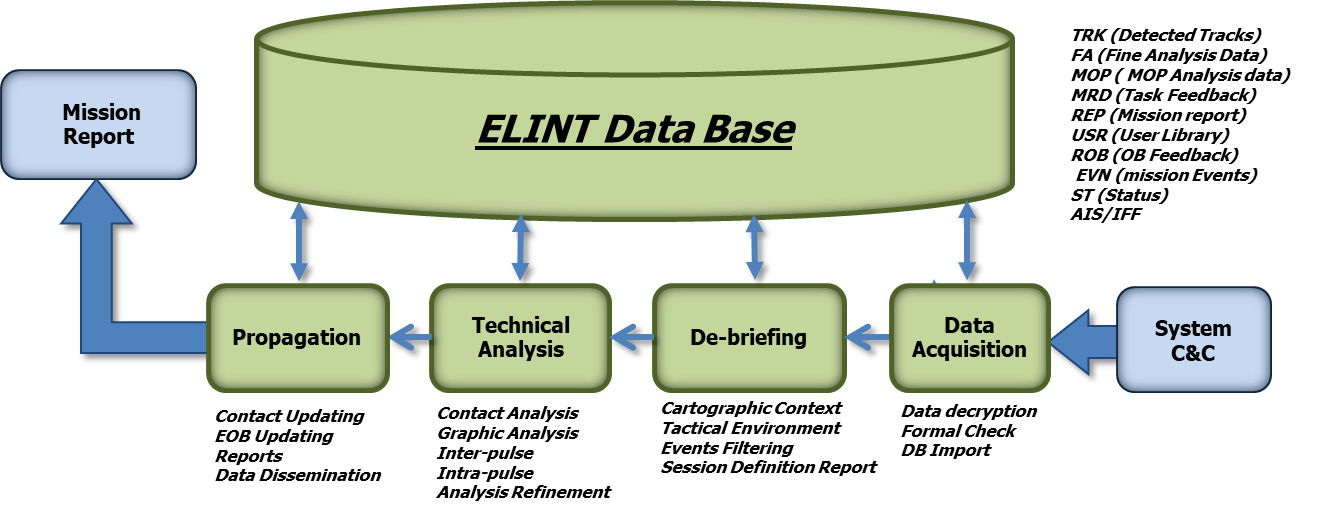
Figure 8: Post Mission Activities
-
ELINT Post Mission Activities
The Post Mission Activities are based on the Data recorded during the mission and are divided in the following phases:
-
-
Data Acquisition: the recorded data are loaded into ELINT DB after having checked and decrypted according to the following steps:
-
Un-formatting: automatically, the recorded mission data selected into common area, they are decoded, decrypted and verified before any further processing.
-
Acquisition: the recorded data are automatically acquired into EW DB, then stored according with the DB structure. Relationship are created with the MDS previously defined for the mission.
-
Statistic Report: the recap about the contents of mission data is automatically produced.
It includes the mission header with some statistic information: number of events, number of detected emitters, number of ELINT analysis, number of system failure, number of AIS platform, and number of IFF platform.
-
-
These data are logically aggregated with those previously defined in the Pre Mission phases.
-
-
De-briefing: the recorded mission reports, the planned tasks and the events are used in order to looking for interesting parts of the mission and marking the analysis sessions.
The Debriefing is designed to support the search for specific segments of the mission, which need to be examined:
-
-
-
-
Cartographic context: the subsystem positions are reported on the map. Dedicated layers will be available for ROB Library and ROB evaluated during the mission. In addition is possible to enable the layer with the environment evaluated for a specific time (active emitters)
-
Chronogram: graphic representation of the time axis of the main events of the mission, the collection of events can be filtered or a specific event can be searched
-
Session Analysis: the session of analysis is defined as time interval, selected by Operator, with the support of the chronogram representation or events delimitation
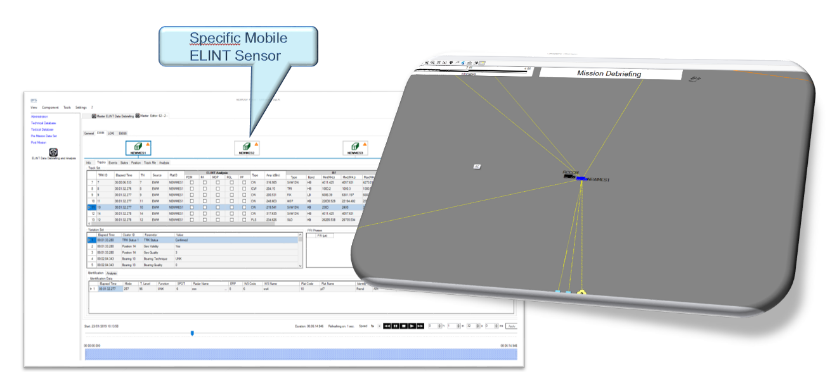
Figure 9: example of Ground ELINT de-briefing
-
Environment Evaluation: using the time scroll bar or time TAG associated with any recorded item, is possible to set the current time and rebuild the corresponding environment
-
-
Analysis: the analysis can be applied on different level of data, raw as intra-pulse and inter-pulse or synthetic as emitters and weapon systems.
The Analysis is a context based on graphical representation of a specific session:
-
-
-
Analysis Session: it is defined with the data belonging to an interval of mission, as defined in the previous debriefing phase.
Contents of any session are one or more ELINT analysis, with collected data (inter-pulse and/or intra-pulse):
-
-
-
-
ELINT Analysis: there are different kind of collection recorded during the mission and available for further processing on the SOSC:
-
Fine Analysis: based on collection of PDM (inter-pulse), designation for their acquisition, tracks extracted and identification result
-
MOP Analysis: based on collection of PDM whit MOP (intra-pulse), designation for their acquisition, MOP extracted
-
Work Flow: with active blocks for the data, their state and origin, with dedicated pop-up menu
-
-
It is possible to iterate analysis activity by filtering the synthetic and raw Data, and store sub-sessions in order to support an incremental analysis.
SOSC can perform analysis activities using the same algorithms resident in the real System.
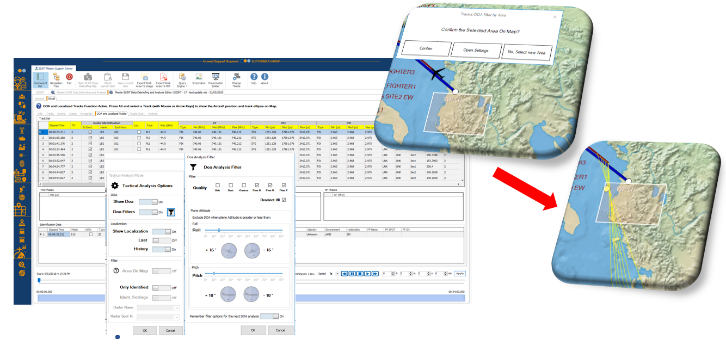
Figure 10: Airborne ELINT Tactical Analysis
-
-
Mission Reporting: represent the capability to produce automatically formatted reports in MS Office Standard representation as Power Point, Word and Excel Data.
During all the activities performed in the SIGINT Operational Support Centre, starting from the acquisition of data from external sources, passing through the planning, generation of libraries, acquisition of the mission restitution, debriefing and analysis, the operator can have a report preparation tool available by acquiring all data of interest produced by the SOSC based on a custom template, it’s possible to include in the report:
-
-
-
-
A screen shot of any type of opened window
-
Custom images
-
Excel data produced by the application
-
-
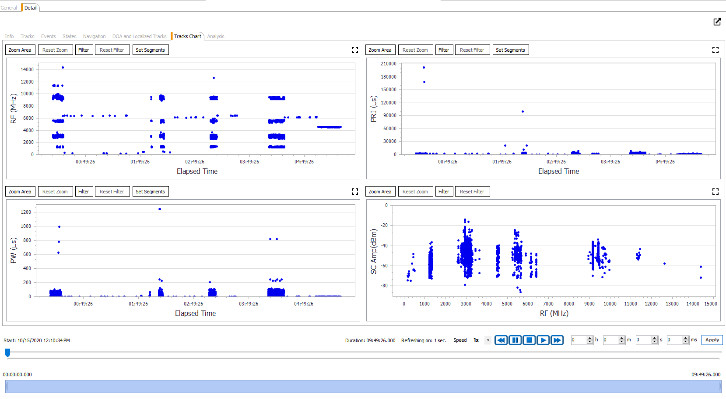
Figure 11: Recorded Tracks Graphical Analysis
It is possible to insert a front page with title and for each power point page, define a title and comment, directly from the presentation builder form.
-
-
Data Base Update: the mission debriefing and analysis results are used to update the central database in terms of technical and tactical entities.
The Analysis can be performed in parallel by several operators.
The result of the Analysis can be one or more updating of the EW DB:-
Updating of parameters of an existing entity
-
Updating of relationship of an existing entity
-
Creation of a new technical or tactical entity
-
Deleting of an entity
-
Creation of a new entity based on User Library
-
-
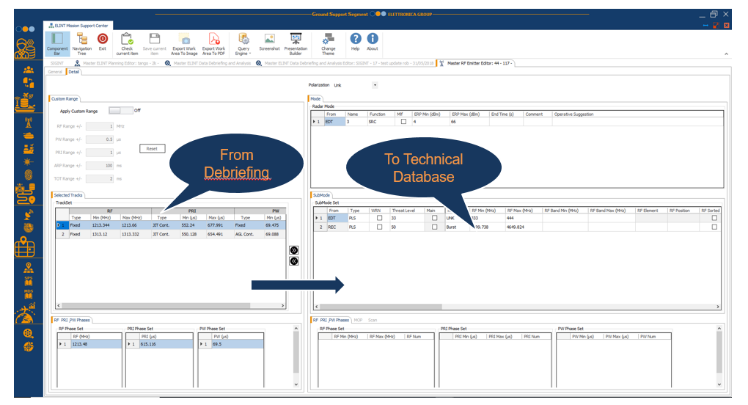
Figure 12: EW DB Update for Tactical Data (Intelligence DB)
All the update activities can be performed in:
-
-
-
Technical way, using the debriefing elaborated data, for example localizations or offline triangulations, or simply the detected tracks, to update directly an existing emitter or create a new one. The same operation can be performed by analysis context.
-
Tactical way, to update an entity or insert a new radar site, unit or installation inside the tactical database, directly from Map or from tabular data.
-
-
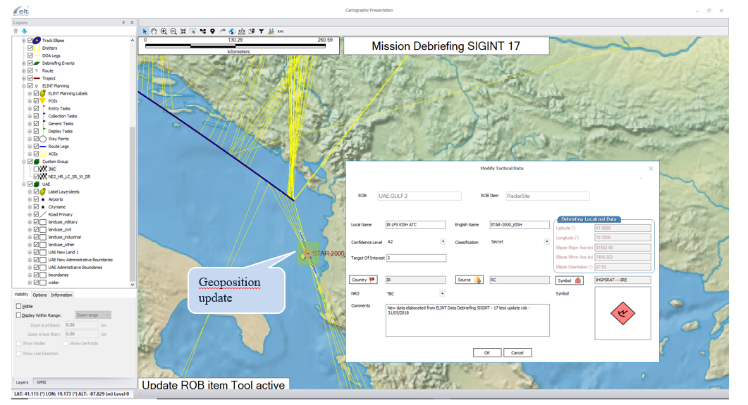
Figure 13: EW DB Update for Technical Parameters
-
- Data Dissemination: the analysis results may be propagated internally to the SIGINT Operational Support Centre by the SIGINT DB updating mechanism or the data can be shared with centralized database entities / centres / national references outside of the SOSC, in different formats according to the Customer needs through formatted reports.
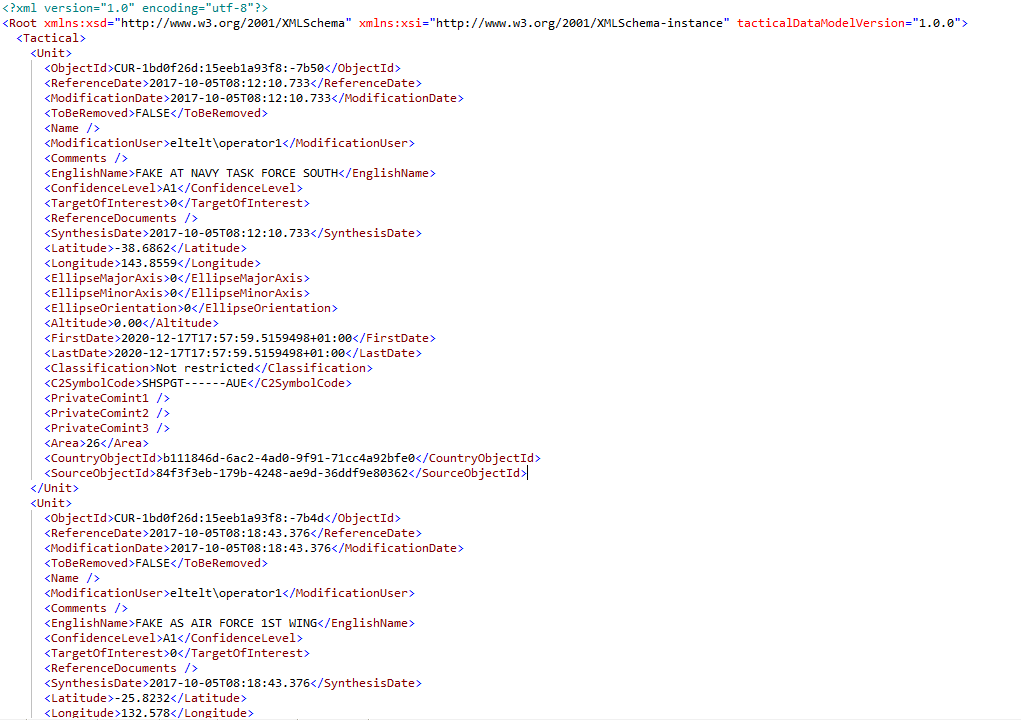
Figure 14: ELINT Data Dissemination by Exchange format