Electronic Support aka electromagnetic Support
The Electronic Support Measures (ESM) equipment usually consisting of two parts:
- Radar ESM (RESM) (usually covering the bandwidth 1.2- 40 GHz) and
- Communications ESM (CESM) (usually covering the bandwidth 80- 3000 MHz).
Due to the different RF surveillance bandwidth and relevant equipment structure (antennas and receivers types). ESM equipment are aboard of all the military platforms and soldier groups to provide alert and protection Implementation from threat.
The ESM, through the detection and signal analysis of the gathered RF emitter radiations, provides the emitter signal characteristics (waveform central frequency (F), bandwidth (BW), duration or pulse width (PW), repetition period (PRI) and the antenna beam pointing revolution period (ARP)).
Those data are compared with the analogue data of the emitters contained in a pre-mission prepared library (Emitter Library) in order to identify the emitter and provide the relevant alerts to the defended platform. Similar operational behavior is performed by the further above recalled.
The RESM platform (except against Low Probability of Intercept Radars [1] (LPIR)) usually exploits a range advantage factor (RAF) in the detection of the radar site with respect to the radar detection range because of its one-way RF wave propagation distance against the two-way RF propagation distance (transmit and receive) of the radar to receive the RESM platform echo.
The two-way RF propagation requires a quite large radar transmitted power, except for the LPIR that exploits long time signal integration in reception.
Typical technical characteristics required for ES equipment are:
- Wide e. m. spectrum (total bandwidth) capability (typically 0.5 to 40 GHz (and now also 90 to 98 GHz) for RESM and 30 to 2400 MHz for CESM)
- Wide dynamic range (60 to >80 dB), to acquire all type of signals,
- Advanced Digital Signal Processing [2], [3] to discriminate/characterize the threat signal of interest from the other ones at close frequencies,
- Quite-accurate angle-of arrival measurement for bearings to locate the transmitter in the environment.
- High-gain receiving antennas [4] to increase LPIR detection probability
Typical ES first level functions:
- Mission Preparation
- Onboard Operational Data base management
- Generation of Mission Libraries
- Files Management
- Mission Execution:
- Radar Interception
- Communication Interception
- Picture Compilation
- Engagement Plan Management
- ES Subsystems Management
- Mission Restitution
- Threat Data Base update
- Row Data recording for off-line Fine Analysis (ELINT & COMINT)
- Training
- Availability of mission simulation
mode on HMI
- Availability of mission simulation
- Maintenance
- BIT diagnostic of ES Subsystems status
RESM Main Functions:
- Radar Warning Receiver (RWR)
detection, discrimination, classification and identification of multiple RF threats, assigning priorities, giving threat alarm and supporting tactical decision against known and unknown emitters
- Emitter Surveillance (ESM)
high accuracy intra-pulse and inter-pulse analysis of emitter parameters
- Data Recording
Filtered (selected Emitters) and not filtered (scenario) raw data recording for Offline “deep” technical analysis
CESM Main Functions
- Detection and DF of communication emissions in the VHF/UHF bands
- Automatic track synthesis and picture compilation
- Localization of selected emitters
- Generation of automatic alerts
- Recording (Narrow Band of selected emitters) and Wide Band (I/Q data of the entire IBW) for Offline “deep” technical analysis
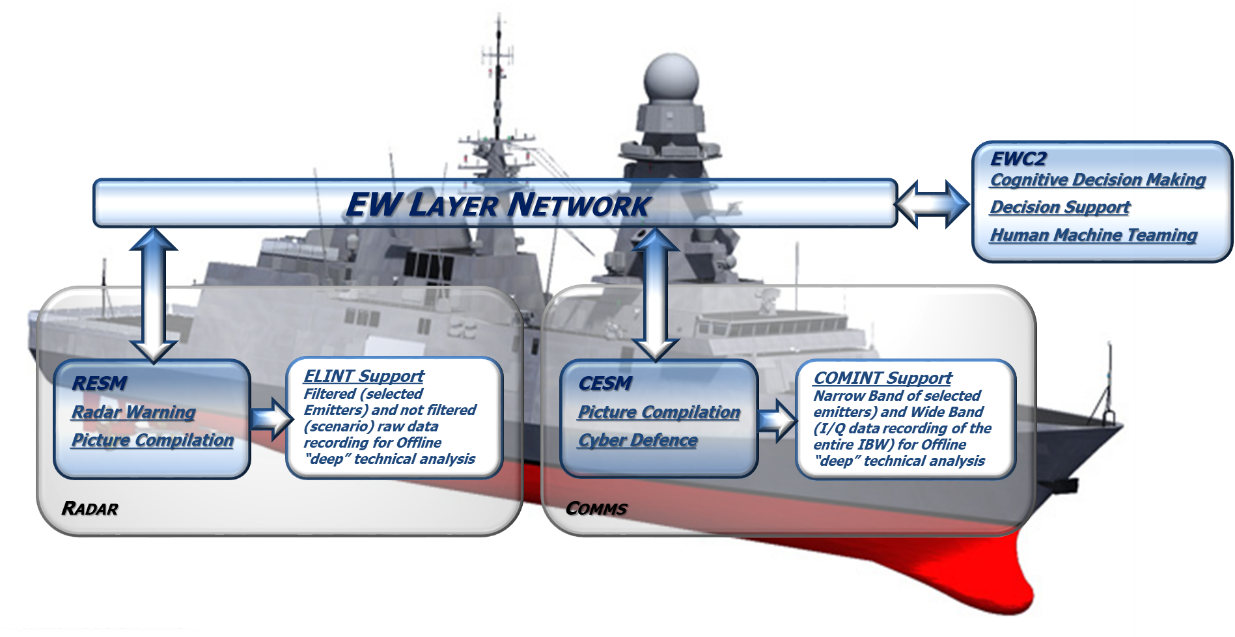
Figure 1: Example of configuration of a Naval ES System
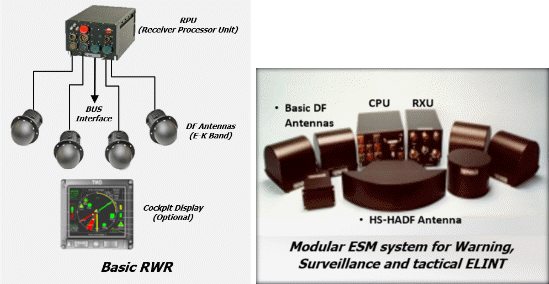
Figure 2: Example of ES Airborne Systems & Figure 3: Example of HELO ES Platform