Electronic Intelligence (ELINT)
Electronic Intelligence focuses its attention on the Radar Systems and to the analysis of their characteristics.
Type of threats: capable of monitoring surveillance, acquisition, early warning, TWS, tracking missile guidance, GCI, Airborne, Ship borne, and all types of weapon system radars.
Type of signals: Pulse, Pulse Doppler, CW, ICW, modern radars using PC (frequency and pulse coding), frequency and PRI agile radars, AM, FM.
System capability:
- Software programmable and computer-controlled system.
- Rapid signal acquisition and data processing with high degree of accuracy.
- Accurate signal analysis and display of emitter activity according to various criteria selected by operator, emitter identification, finger printing (inter and intra-pulse analysis).
- Correlation and maintenance of data library, accurate localization of radars, capability to transfer the recorded data / processes data through the separate encrypted airborne data link in near real time.
- Capability of GPS time stamping every 1 second all recorded data.
Electronic Intelligence can be both tactical and technical: when tactical, the ELINT equipment is optionally associated within a weapon system into an Electronic Support Measure (ESM) suite, and it enables the detection and passive geo-localization.
For a deeper signal investigation activity (content acquisition and analysis and off-line identification) a technical analysis is required.
- Tactical Operations: Military organization Army, Navy, and Air Force, are interested in identify the location and capability of all enemy radars. This is referred to as the Radar Order of Battle (ROB).
This is important, for example, for the Air Force, they must know where and how the enemy radars are organized so that they can plan how to defeat them or take proper countermeasures against them.
Example of Tactical Presentation is given in Fig.1.
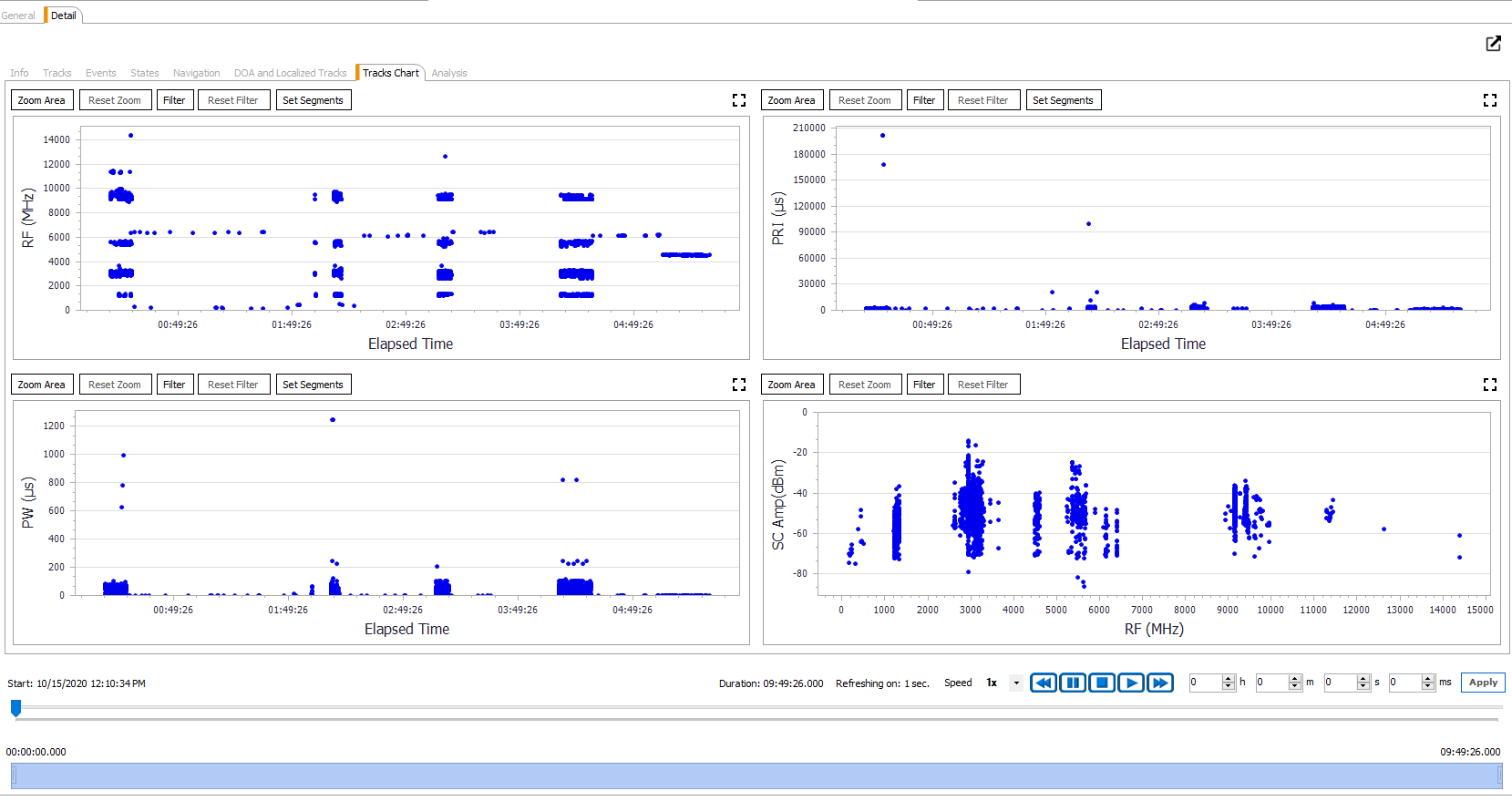
Figure 1: Notional Presentation of Tactical Information (ROB)
- Technical Operations: Intelligence instead is aiming to analyze the enemy radars capturing all the radar mode of operation and waveforms, this is mandatory for understanding how defence systems work, to identify new radars and new operational modes in order to follow the evolution of new enemy electronic developments and equipment.
Example of Technical Presentation is given in Fig.2.
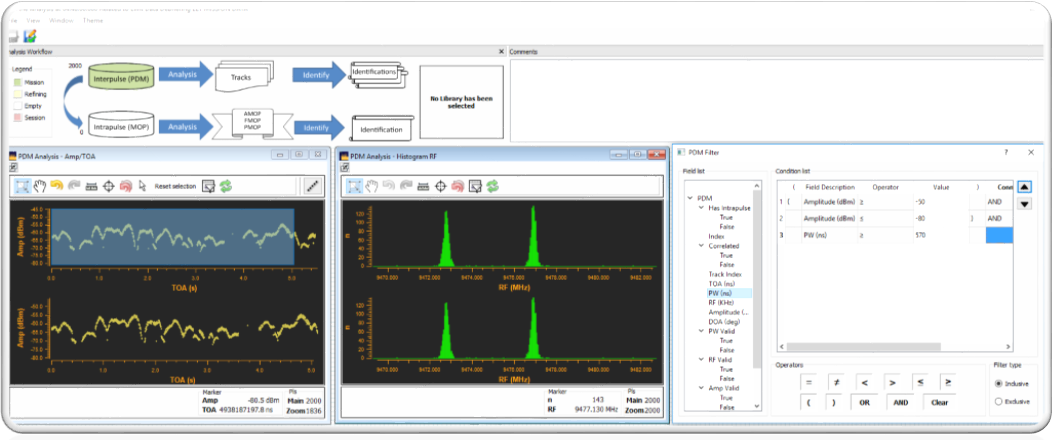
Figure 2: Notional Presentation of Technical information
To support these different views an ELINT System need to have specific characteristics like:
- Detect and locate Radar Emission in a specific area of interest (AOI)
- monitor the full electronic spectrum envelope
- operate far away from the enemy installations
- provide detailed information’s and parameters concerning the enemy radar
To fulfill these operational requirements an ELINT System usually integrates two types of receivers:
- Panoramic Receiver (Wide Band Receiver, WBR), used for monitoring the environment.
- Selective Receiver (Super Heterodyne Receiver, SHR), used for measuring the radar waveforms.
The result of the ELINT Technical Analysis, for Radars associated with weapon systems (search and tracking radars) and missile seekers, leads to the constitution of weapon systems databases, which are downloaded into the mission databases of the EW self-protection systems of combat platforms to contribute to the identification process.