Deception Jamming (Deception Techniques in Radar ECM)
The deception action consists in the transmission of signal as similar as possible to the original source.
These techniques are coherent and based on the reception and re-transmission of the signal coming from the radar with additional modulations (frequency, time) superimposed (they are DRFM based).
The resultant waveform is coherent and naturally matched with the radar receiver that will not be able to discriminate it from the real echo.
Its intensity must be sufficient to overwhelm the radar target echo and to “deceive” the radar receiver in order to synchronize it with the “false” transmitter with no evidence of the replacement, at waveform level.
The deception is mainly a coherent technique, whose waveform is generated by a DRFM (Digital radio Frequency memory), that consists in:
a. Receiving and storing (in a digital memory) the samples of the radar signal (the storage can be maintained for a long time without loss of information).
b. Retrieving the stored signal after the programmed time, elaborating it with superimposition of modulation (frequency, phase, etc…) and
c. Retransmitting the manipulated signal towards the radar receiver
In case of non-coherent deception technique, points a. and b. above are replaced by the direct synthesis of the carrier frequency of the jamming/deception signal.
Domains of application of deception techniques are relevant to Range, Doppler, Amplitude, and Angle:
• Range Domain: Range Gate Pull Off (RGPO), Range Gate Pull In (RGPI),
• Doppler Domain: Velocity Gate Pull Off/In (VGPO/I)
• Range/Doppler: Coordinated RVGPO
• Multiple False Targets (MFT):
◦ Range: Multiple RGPO/I
◦ Doppler: Multiple Doppler False Targets (MDFT)
◦ Range/Doppler: Multiple Range Doppler False Targets (MRDFT), Coordinated RVGPO
◦ Spoofing (coherent or not-coherent false targets)
• Amplitude Domain: On Off (or swept amplitude modulation), Count Down
• Angle Domain: Inverse Gain, Beam Scan Modulation (Fixed or Swept Poke up gate), Cross Eye , Cross Pol
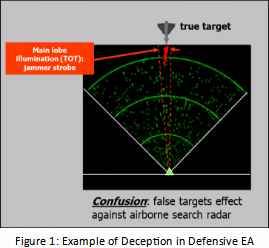
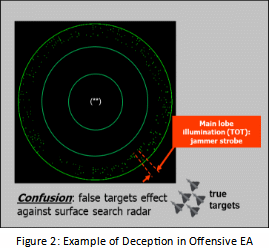
A good example of deception, used both in defensive and offensive EA, is given by the combination of some of the above-mentioned techniques that generates a number of false targets surrounding the real one/ones, made by a synchronized mix of MDFT with coordinated Multiple RGPO/I
The purpose of this combined technique is to engage the radar receiver and processing resources with a number of “credible” false signals to mask the platform to be protected (Defensive Electronic Attack, Figure 1) or to create a “free” Electro Magnetic corridor for the intruder attack package (Offensive Electronic Attack, figure 2).