Barrage Noise
Barrage Noise is a self-screening or support-jamming technique that transmits a noise-like signal over a wide RF band for masking signals received by a victim electronic system.
Barrage Noise transmission spreads noise-like jamming energy across a wide frequency band such that frequency-agile radars can be jammed over their whole agility bandwidths or many victim radars can be jammed simultaneously. Bandwidths ranging from the order of 100 MHz to an octave are considered barrage.
The disadvantage of Barrage Noise is that only a fraction of the jamming power enters the radar receiver.
However, this form of jamming is the most effective if the required power density at the radar receivers can be achieved because is not intelligence-sensitive (it does not need a good a-priori knowledge of the threat) like many forms of smart noise and deception jamming schemes.
Barrage Noise waveforms are obtained through the transmission of a carrier modulated by noise.
Jamming carrier can be generated in one of the following ways :
- Non-coherent:
– through digital synthesis of a carrier at the agility centre frequency of the countered radar track
– through synthesis of multi band/multi-lines spectrum. - Coherent:
– through detection and memorization of the threat radar signal
Barrage Noise modulation can be generated in different ways:
- Direct amplification of low power source (amplification of noise generated by a resistor or diode)
- High power voltage controlled oscillator (BWO) frequency modulated by a fast sawtooth voltage waveform: the spectrum is line periodical spectrum (comb) spaced by sweep speed
- Modified Swept Noise (also Swept Spot Noise) uses a sawtooth frequency modulation plus an additional noise FM and an additional noise AM (contiguous subcarrier barrage noise).
- Pseudo-Random, the frequency modulation is generated by pseudorandom waveforms jumping randomly between discrete levels.
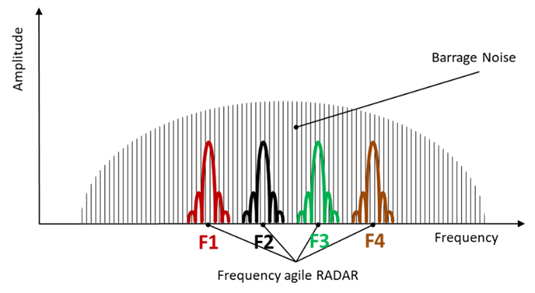
Figure 1: Barrage Continuous Noise
Noise Jamming Techniques can be combined with different types of modulations to increase jamming effectiveness.
Frequency Modulation is usually part of noise generation.
Amplitude modulation can be of several types:
- Slow increase/decrease: to take control of radar AGC or to gradually hand over AGC control to other signals or to chaff/decoy
- Swept audio modulation (also known as Scan Rate Modulation
- Swept Scan Band, Noise Swept Audio, LORO deception, SORO deception, Swept Square Wave
- Inverse Gain
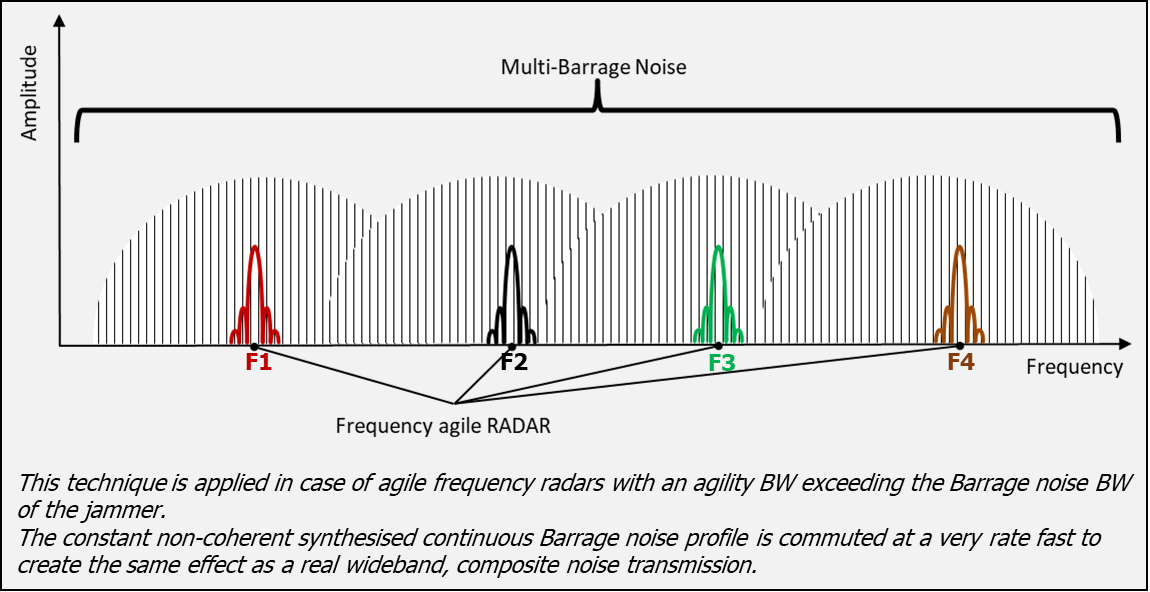
Figure 2: Hopping Multi-Barrage Noise